Inflammation is a natural immune response that helps the body fight off harmful stimuli. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to the development and progression of various diseases. In this post, we will explore:
- The biological basis of inflammation as the root of disease
- The link between inflammation and specific diseases
- Strategies for reducing inflammation and preventing disease
Inflammation is a natural immune response that occurs when the body detects harmful stimuli such as pathogens, toxins, or damaged cells. This response is triggered by a complex network of signaling molecules, cells, and tissues that work together to eliminate the threat and initiate tissue repair. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to tissue damage, organ dysfunction, and the development of various diseases; including, but not limited to, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer.
For example, chronic inflammation can lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries. This can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Similarly, chronic inflammation can impair insulin signaling and promote insulin resistance, which can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, chronic inflammation has also been linked to the development and progression of cancer. Inflammation can damage DNA, promote cell proliferation, and impair immune surveillance. All of which can contribute to the development and spread of cancer. Furthermore, chronic inflammation can also create a microenvironment that supports tumor growth and metastasis.
Chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation is often the result of prolonged exposure to environmental and lifestyle factors such as smoking, pollution, stress, and poor diet. These factors can activate the immune system and trigger a persistent inflammatory response that damages tissues and promotes disease. Moreover, chronic inflammation can also lead to the accumulation of immune cells, cytokines, and other inflammatory mediators that further exacerbate tissue damage and inflammation.
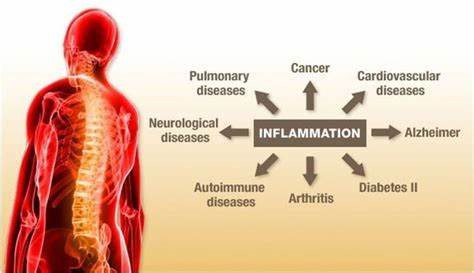
Reducing inflammation
Reducing inflammation is an important strategy for preventing and treating various diseases. One approach is to adopt an anti-inflammatory diet and lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. An anti-inflammatory diet includes foods that are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and fatty fish. Pharmacological interventions targeting inflammation can also be effective in reducing inflammation and preventing disease. For example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen can reduce inflammation and lower the risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer. That said, these should not be considered for long-term use.
Moreover, drugs that target specific inflammatory pathways such as cytokines and chemokines are being developed and tested for various inflammatory diseases. Early detection and treatment of chronic inflammation is also crucial for preventing disease. Regular check-ups and monitoring of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) can help identify individuals at risk for chronic inflammation and allow for early intervention and treatment.



Leave a Reply